
We expect computers to be precision machines running millions of lines of code without breaking a sweat. But now and then, even the smartest software stumbles. History is a living proof that computers cannot always be reliable. Here’s a list of infamous software fails that caused chaos and cost billions.
Therac-25 Gave Deadly Radiation Doses

A software race condition in the Therac-25 radiation therapy machine led to tragic consequences in the 1980s. At least six patients received massive overdoses of radiation due to a bug that bypassed safety interlocks. In some cases, no error messages appeared at all, making it difficult for operators to detect the issue.
Mariner 1 Lost Its Flight Path

In 1962, NASA’s Mariner 1 was set to become the first U.S. spacecraft to explore Venus. But just 293 seconds after launch, it had to be deliberately destroyed. The culprit was a missing overbar in a guidance equation. This minor typographic error caused the rocket to veer dangerously off course.
Ariane 5 Exploded Mid-Air Launch
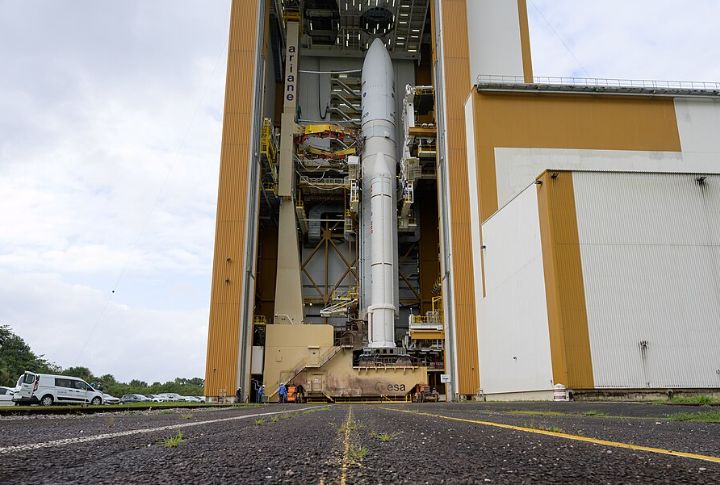

Just 37 seconds after taking off on June 4, 1996, the European Space Agency’s Ariane 5 rocket broke apart. Engineers had reused software from the Ariane 4 without testing it for the new rocket’s conditions. A data conversion overflow triggered the self-destruct mechanism, resulting in the loss of the mission and $370 million in damages.
Y2K Confused Date Logic Worldwide
The infamous Y2K bug emerged from the assumption that years could be safely coded with just two digits. As 1999 rolled into 2000, computers worldwide faced logic errors. Some banking systems failed, elevators stalled, and a Japanese nuclear plant’s safety system crashed. A global effort costing over $300 billion helped prevent major catastrophes.
Toyota’s Sudden Acceleration Crisis

Toyota recalled about 9 million vehicles due to reports of unintended acceleration between 2009 and 2011. NASA was brought in to inspect the electronic throttle systems and found software bugs embedded deep within the firmware. These glitches were linked to 89 fatalities and hundreds of injuries.
Windows ME Froze Like A Statue
Released in 2000, Microsoft’s Windows ME (Millennium Edition) quickly gained notoriety for being unstable and prone to bugs. Users experienced constant crashes and system freezes just by plugging in a USB device. Even Microsoft developers reportedly avoided using it. It was so unreliable, users dubbed it the “Mistake Edition.”
NASA’s Spirit Rover Misread Memory Space

The Spirit rover began rebooting endlessly shortly after landing on Mars in 2004. Engineers discovered that its flash memory had become overloaded with unnecessary files, causing it to enter safe mode. NASA had to rewrite the rover’s memory handling remotely. Despite the rocky start, Spirit went on to operate for over six years, beyond its 90-day mission lifespan.
T-Mobile’s Billing Glitch Cost Millions

A software bug in T-Mobile’s billing system led to customers being charged for services that were supposed to be free. The FCC fined T-Mobile for deceptive billing practices after public outcry. Some users didn’t notice the overcharges for months. Millions were eventually refunded.
Robinhood Crashed During Historic Market Surge

During a high-stakes trading day in March 2020, the Dow’s most significant point gain in history, Robinhood users found themselves locked out of the app. A system overload, caused by unprecedented trading volume, led to the outage. One user reportedly missed out on a $50,000 gain. Robinhood attributed the failure to a “stress on infrastructure.”
Cloudflare Firewall Glitch Took Down The Web
Cloudflare’s firewall update introduced a misconfiguration that triggered widespread internet outages in June 2019. Sites like Shopify and news outlets went dark. Since Cloudflare handles roughly 10% of global internet traffic, the effects were widespread. Engineers rolled back the faulty update within 30 minutes.
Okta Data Breach Exposed Sensitive Credentials

In 2022, identity management company Okta suffered a breach when hackers exploited a third-party support account. Admin credentials were compromised, and screenshots of internal tools were leaked online. Since Okta serves major companies like Cloudflare and 1Password, the breach raised serious concerns.
Boeing 737 Max Crashes Linked To Software

The Boeing 737 Max was involved in two devastating crashes in 2018 and 2019, killing 346 people. Investigations revealed that the MCAS (Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System) software misinterpreted faulty sensor data and forced the plane’s nose downward. Worse, pilots weren’t fully informed about the system.
Knight Capital’s Trading Bot Burned $440 Million

A faulty trading algorithm at Knight Capital Group disrupted the stock market in 2012 by flooding it with millions of incorrect orders. Within just 45 minutes, the company lost $440 million. The glitch was traced to outdated code being reactivated unintentionally, and the incident nearly bankrupted the firm.
Healthcare.gov Crashed Under Real Load
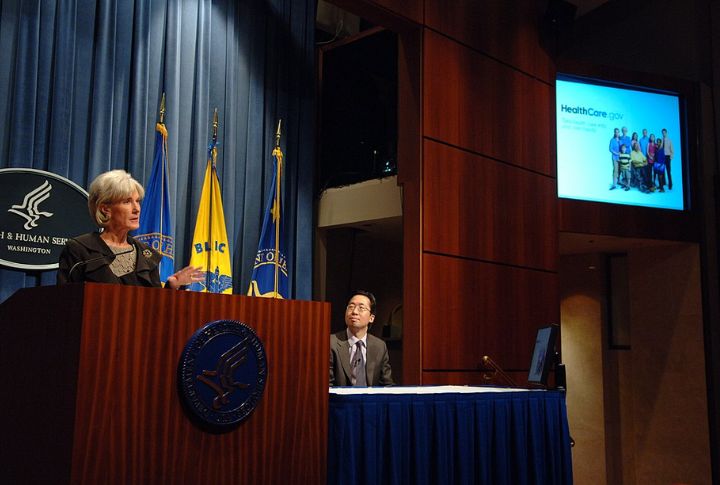

When the U.S. government launched Healthcare.gov in October 2013, it was supposed to be a gateway to affordable health insurance. Instead, it became a case study in how not to launch a website. Within minutes of going live, the site crashed under the weight of over 4 million visitors.
Heartbleed Left Data Wide Open
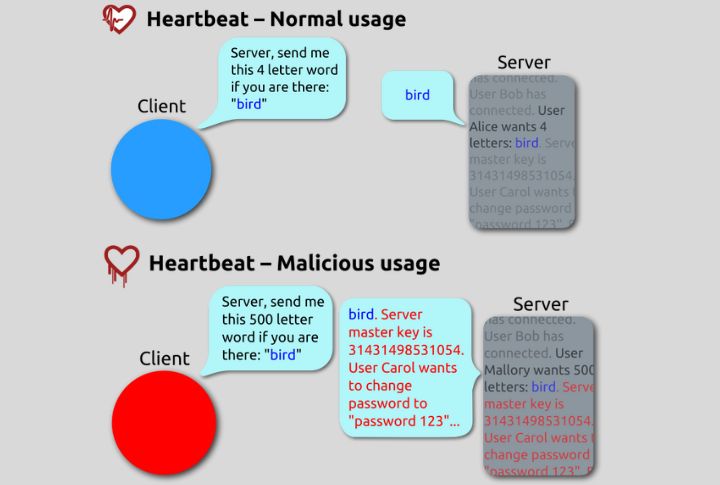
In 2014, a vulnerability in the OpenSSL cryptographic library known as Heartbleed sent shockwaves across the internet. The bug allowed attackers to read random chunks of a server’s memory, exposing passwords and even private encryption keys. Major websites like Yahoo and even government portals were affected.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Exploded Repeatedly

The Galaxy Note 7 was Samsung’s flagship smartphone in 2016. But it became a global punchline. Poor battery design, compounded by aggressive power management software, led to the devices overheating and exploding. Samsung recalled 2.5 million units, then issued a second recall when replacement phones caught fire too.
Tesla Autopilot Failed On Curved Roads

Tesla’s Autopilot software has been hailed as a step toward self-driving cars. In multiple cases, the system misread lane markers on curved roads, steering vehicles directly into barriers or oncoming traffic. At least two fatal crashes were tied to this recurring issue. Despite warnings, Tesla continued real-world beta testing with live drivers.
Uber’s Algorithm Overcharged Holiday Travelers

During holidays and natural disasters, Uber’s surge pricing algorithm sometimes took “demand-based pricing” to unethical extremes. In one infamous case, riders were charged over $100 for trips that usually cost $20. Public backlash led to class-action lawsuits and forced Uber to cap prices during emergencies.
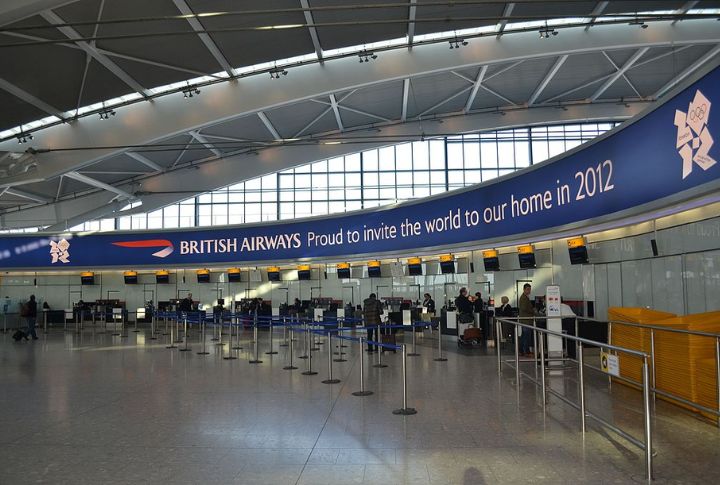
British Airways Grounded By IT Breakdown

In May 2017, a power surge at British Airways’ data center triggered a massive IT system failure. Flights were canceled, and over 75,000 passengers were stranded worldwide. The estimated cost was around $100 million. Staff were forced to resort to manual check-ins and handwritten boarding passes.
Cash App Doubled Payments Randomly

A glitch in Square’s Cash App backend caused several users to be charged twice for transactions, both in peer-to-peer transfers and merchant payments. Some saw hundreds of dollars debited unexpectedly, prompting panic and fears of account hacks. Refunds took days to process, further damaging user trust.

