How often do we pause and think about how amazing our bodies truly are? Our bodies are like incredible machines, with millions of things happening inside them every second—all working together to keep us healthy and alive. Our skin heals itself after a tiny paper cut. And our eyes can tell the difference between 10 million shades of color! These are just a few of the incredible things. Here are 15 surprising facts about the human body!
Your Stomach Gets a New Lining Every Few Days

Your stomach is packed with powerful acids that are tough enough to break down your food. But here’s a wild fact: those same acids are strong enough to digest your stomach itself! To keep this from happening, your stomach has a clever trick—it creates a fresh layer of protective mucus every few days. The old lining gets swapped out with new cells in a process that takes about 3 to 4 days.
Your Bones Are Stronger Than Steel

It might sound crazy, but pound for pound, bone is stronger than steel, meaning it can withstand comparable pressure. A single cubic inch of bone can bear the weight of about five standard pickup trucks. This strength comes from its special makeup: a mix of collagen, which keeps things flexible, and calcium phosphate, which makes it super tough. However, steel is still stronger by volume, making this comparison context-dependent.
You Shed 40,000 Skin Cells Every Hour
Your skin is always working hard to protect you from the outside world, injuries, and nasty infections. Every hour, you shed around 40,000 dead skin cells—that’s close to a million cells a day! The outer layer of your skin, the epidermis, is made up of tough, dead skin cells continuously being shed and replaced. In fact, your skin completely renews itself about once a month.
Our Attention Span Might Have Dropped to 8 Seconds

A 2015 Microsoft study suggested that our attention span might have dropped to 8 seconds due to the fast-paced digital world. However, this was more of a reflection on how technology affects our ability to stay focused rather than a fixed measurement. Though we’re bombarded with constant information from phones and devices, humans are still capable of deep, sustained focus when necessary.
Your Heart Can Beat Outside Your Body
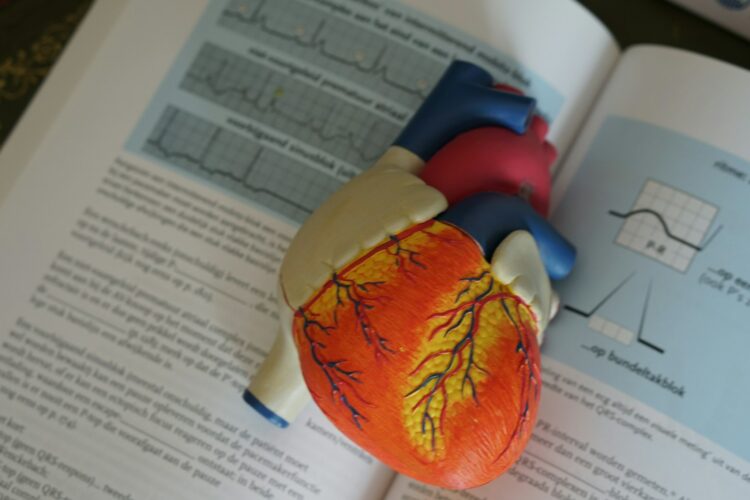
The heart is an incredible muscle that doesn’t even need the brain to keep beating. It has its own built-in electrical system, called the cardiac conduction system, that keeps it pumping. Thanks to this setup, the heart can keep beating independently—even outside the body—as long as it gets enough oxygen. That’s why heart transplants work! This ability to run on its own makes the heart one of the coolest and most unique organs in our body.
You Produce Enough Saliva to Fill Up About 500 Bathtubs in a Lifetime

Saliva is often underrated, but it’s essential for digestion and oral health. An average person produces between 0.5 to 1.5 liters of saliva daily, adding up to about 20,000 liters over a lifetime—enough to fill around 500 bathtubs, not two swimming pools. Saliva has enzymes that kickstart digestion and acts as a natural mouthwash by fighting off bacteria.
Your Nose Can Detect Over a Trillion Smells

The human nose is way more impressive than we used to think. A 2014 study from Rockefeller University suggested that humans could detect up to a trillion smells. However, some researchers have since debated this figure, and the exact number is still under discussion. Regardless, we can detect a vast range of scents, making our sense of smell an essential part of survival and memory.
The Small Intestine Is Actually Quite Long

Even though it’s called the “small” intestine, it’s actually about 20 feet long, making it the longest part of your digestive system. Its main job is to soak up nutrients from the food you eat. To do this really well, it has a huge surface area—thanks to tiny, finger-like projections called villi and microvilli that line its walls. If you spread it out flat, it would cover a whole tennis court, making sure you absorb all the vitamins, minerals, and nutrients your body needs.
Humans Are Bioluminescent

It might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but humans emit a tiny amount of light due to biochemical reactions in the body. Researchers at Kyoto University discovered this light is incredibly faint—about 1,000 times dimmer than what our eyes can detect. This bioluminescence is real but not visible to the naked eye.
The Human Body Contains Enough Iron to Make a Small Nail
Iron is super important for our health, and our bodies have about 3 to 4 grams of it. Most of this iron is in our blood, where it helps make hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen. If you could pull all the iron out of your body, it would be enough to make a small nail. Without enough iron, you could end up with anemia, which shows just how crucial this element is for keeping us energized and healthy.
Babies Have More Bones Than Adults

Newborn babies start out with about 270 bones, but some of these merge as they grow. By the time they’re adults, the number drops to 206. This merging helps create a strong yet flexible skeleton that protects our organs, allows us to move, and supports our body weight.
You Have Tiny Mites Living on Your Skin
Tiny creatures called Demodex mites live in almost every adult’s pores and hair follicles. These little mites are harmless and have a pretty simple job—they feed on dead skin cells and the oils produced by our skin. While it might sound unsettling to think about mites hanging out on us, they play a helpful role. Munching on dead skin and excess oil helps keep our skin’s ecosystem balanced and in check.
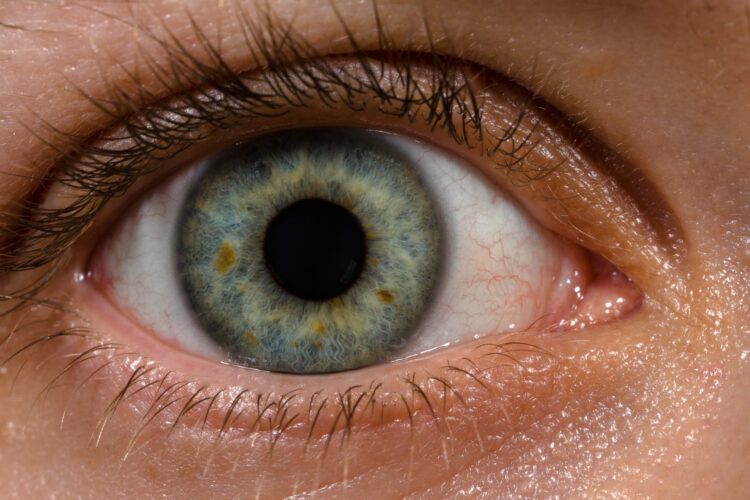
Your Eyes Can Distinguish About 1 Million Different Colors.

The human eye is a marvel of evolution. Thanks to millions of cone cells in our retinas, we can distinguish roughly 1 million different colors. This ability is super important for recognizing faces, reading emotions, and enjoying the vibrant beauty around us. While the number of distinguishable shades can vary from person to person, our color vision is still among the most advanced in the animal kingdom.
The Brain Is More Active at Night Than During the Day
Contrary to what a lot of people think, our brains don’t just “turn off” when we sleep. In fact, during certain sleep stages—especially REM (rapid eye movement) sleep—our brains are even more active than when we’re awake. It’s in these stages that our brains process emotions, solidify memories, and tackle tricky problems.
Human Hair is Nearly Indestructible

Hair is mostly made up of a protein called keratin, which you’ll also find in animal hooves and feathers. Besides being flammable, hair doesn’t break down easily and can stand up to a lot of chemicals and environmental conditions. This toughness is why you often find intact hair on ancient remains and archaeological digs, giving us a treasure trove of information about past civilizations.

