
Some empires outgrew their neighbors by sheer force or smart diplomacy. Their size changed how history unfolded, stretching their control across continents. Behind their growth were bold decisions, unique leaders, and shifting alliances. This article traces the footprints of history’s largest empires and how they became central to the world’s political and cultural evolution.
The British Empire Dominated Global Geography
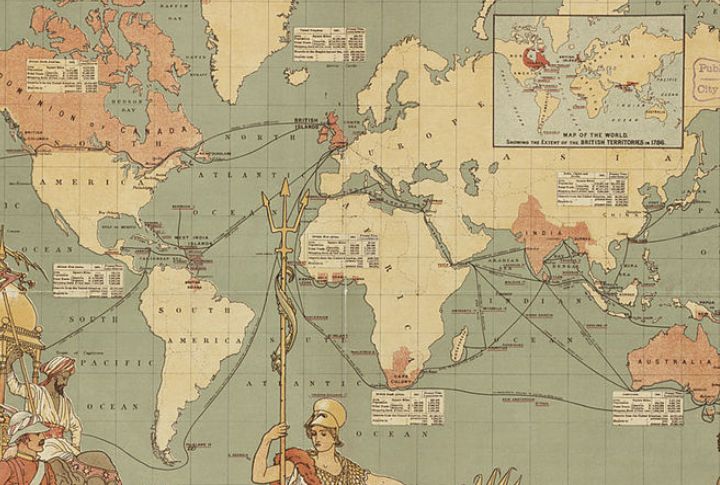
Incredibly, the British Empire once spanned 24% of the world’s landmass at its peak in 1920. Data from a study led by eminent historians shows that the British governed roughly 23% of the global population, which was over 400 million people. Its legal systems still shape over 50 countries today, including Australia, New Zealand, India, and others.
The Mongol Empire Connected East And West

It’s worth noting that the Mongol Empire remains the largest contiguous land empire in history. Under Genghis Khan, it stretched from the Pacific Ocean to Eastern Europe. Postal stations placed every 25 to 45 miles ensured smooth communication. The empire also played a pivotal role in reviving the Silk Road and fostering a new era of global trade.
The Roman Empire Shaped Western Civilization
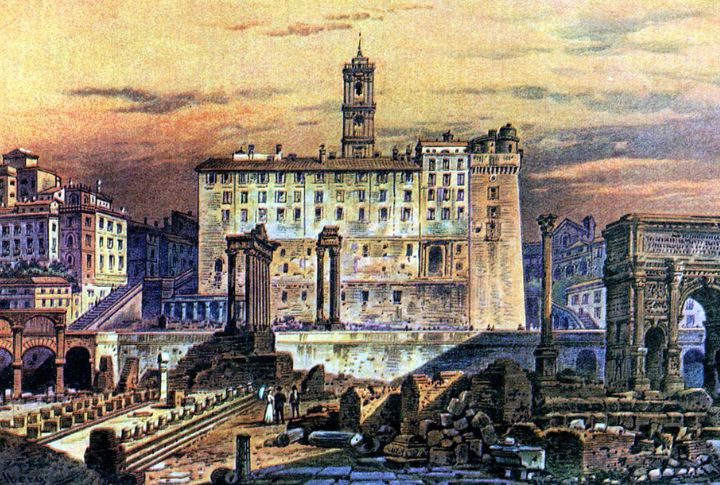
The Roman Empire helped lay the foundations of Western civilization. At its height, it spanned three continents that covered roughly 5 million square kilometers. Roman governance laid the groundwork for modern democracies. Innovations like running water, apartment buildings, and postal services emerged in its cities. Remarkably, some roads built by the Romans continue to serve travelers to date.
The Qing Dynasty Was Earth’s Largest In The 18th Century

The Qing Dynasty was the final chapter in China’s imperial story. It controlled an immense territory of over 13 million square kilometers. Its legacy includes the Forbidden City, a palace designed with 9,999 rooms. This architectural marvel showcased imperial grandeur, infused with layers of Chinese traditions.
The Umayyad Caliphate Ruled From Spain To India
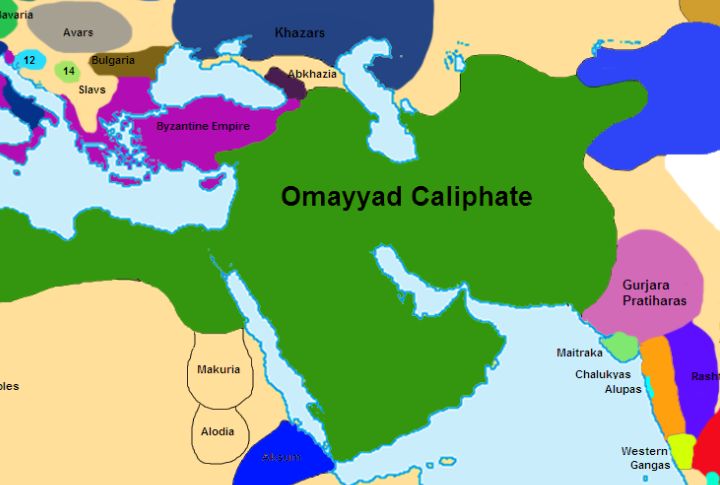
The Umayyad Caliphate stretched from Spain to India and became the largest Islamic empire by territory. Arabic served as its official language. Cordoba, the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate in Al-Andalus, introduced streetlights long before European cities. It also carried paper-making practices from China to Europe.
The Russian Empire Bridged Europe And Asia

By the late 19th century, the Russian Empire stretched across 22 million square kilometers, shaping Eurasian politics for centuries. Its rulers pushed modernization. Interestingly, Peter the Great even taxed beards to enforce Western styles. The empire’s reach was vast, once including Alaska, which it later sold to the United States in 1867.
The Mali Empire Dominated West African Trade

This empire’s power came from controlling the gold and salt trade routes across the Sahara. Additionally, the wealth of the empire peaked under Mansa Musa, considered the richest man in history. His 1324 pilgrimage to Mecca caused economic chaos with an oversupply of gold. Timbuktu, under Mali’s rule, emerged as a global center of Islamic scholarship.
The Spanish Empire Brought The Americas Into A Global Network

For over two decades, Spain controlled much of Central and South America. This wave of colonization sparked the Columbian Exchange. Suddenly, different resources were moving between continents like never before. Additionally, Spanish galleons created the first trans-Pacific trade route between Mexico and the Philippines, thereby linking economies and cultures in unprecedented ways.
The French Empire Redefined Culture Through Global Reach

The French Empire is notable in history for spreading its cultural influence across Africa, Southeast Asia, the Caribbean, and Canada. French civil law remains the cornerstone for legal systems in over 40 countries. In West Africa, colonial schools taught local languages alongside Latin and philosophy. It helped shape a legacy of education that continues to touch minds across generations.
India’s First Empire That Shaped Asia
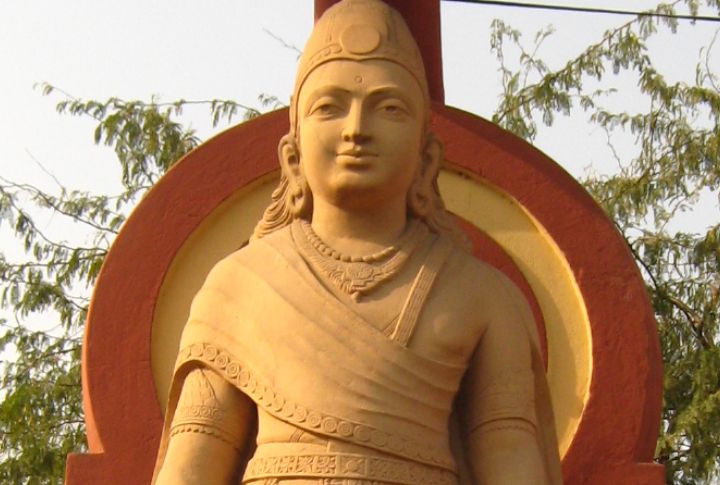

Founded in 321 BCE by Chandragupta Maurya, the Maurya Empire became the largest empire in ancient India. Spanning over 5 million square kilometers, it unified vast regions. Under Ashoka’s rule, Buddhism spread across Asia, shifting the empire’s focus. His governance emphasized religious tolerance, justice, and fair treatment, which left a lasting cultural imprint across the region.

