Mars might look like the next frontier, but don’t let those warm pictures fool you. It’s no place for the unprepared. Beneath the sci-fi dreams lie real, dangerous barriers. Know what they are? Here are the top 10 challenges that show just how far we are from calling the Red Planet home.
Questionable Water Sources
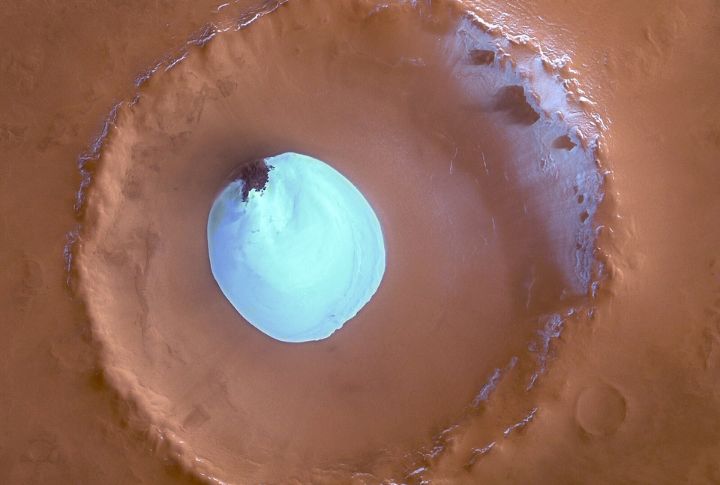

Survival on Mars hinges on access to liquid water. Even though ice has been found, it’s insufficient for sustaining life. The real breakthrough lies in locating underground water, which could support long-term missions and make colonization a more achievable goal for future explorers.
Lack Of Oxygen

The planet’s thin atmosphere leaves little room for human life. Oxygen is nearly absent, so breathing unassisted is out of the question. Interestingly, future technologies to create breathable air or alter the atmosphere through terraforming may offer hope for long-term habitation.
Extreme Temperatures

A planet of extremes, Mars endures temperature swings from freezing nights to surprisingly warm days. To survive such harsh fluctuations, human settlers must build advanced habitats that insulate against the intense cold while managing the rare but dangerous heat surges. Without proper protection, life there wouldn’t last long.
Absence Of Magnetic Field
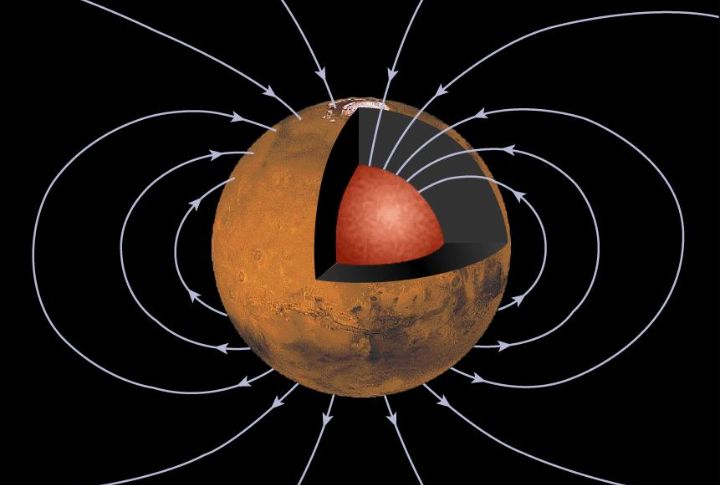
Humans need protection from harmful solar radiation that damages our cells and DNA. Earth’s magnetic field shields us from that danger. However, Mars can’t offer that protection due to the absence of a magnetic field. It presents a challenge for long-term human habitation.
Incompatible Soil Composition
The Red Planet’s soil, rich in iron oxide, doesn’t naturally support plant life. To grow food, scientists must alter the soil composition or create artificial farming environments. Innovative farming or soil culture will play a key role in converting Mars into a more hospitable place.
Circadian Rhythm Disruption
Mars has this circadian rhythm disruption. This means that the planet’s day is about 24.6 hours, which is slightly longer than Earth’s. Its weak gravity and limited sunlight exposure can reduce our natural sleep-wake cycles, impacting health, cognitive function, and overall performance.
Heavy Energy Needs

Creating safe environments and running essential systems will depend on a powerful energy source in such an inhospitable environment. But since the Sun’s distance makes solar power unreliable, there is a need for stronger alternatives, such as nuclear energy.
Adverse Health Impacts
Even if a suitable atmosphere is established, living on Mars can cause significant physical stress, leading to muscle atrophy, loss of bone density, and weakened immunity. Addressing these challenges will require advanced medical technologies and effective countermeasures to ensure settlers stay healthy.
Dust Storms
Dust storms on the Red Planet can rage for months, reducing visibility. Moreover, intense storms can damage critical equipment and make conditions nearly unlivable. Shielding habitats and gear from this abrasive force is vital for anyone hoping to endure life there.
Life Support Backup

Life support systems must be self-sustaining. The equipment will need to manage air, water, and food recycling without requiring frequent visits to Earth. Also, backup mechanisms are not optional—they are essential safeguards. Any failure in these systems could jeopardize human life.

